1099. Build A Binary Search Tree (30)
时间限制
100 ms
内存限制
65536 kB
代码长度限制
16000 B
判题程序
Standard
作者
CHEN, Yue
A Binary Search Tree (BST) is recursively defined as a binary tree which has the following properties:
-
The left subtree of a node contains only nodes with keys less than the node's key.
-
The right subtree of a node contains only nodes with keys greater than or equal to the node's key.
-
Both the left and right subtrees must also be binary search trees.
Given the structure of a binary tree and a sequence of distinct integer keys, there is only one way to fill these keys into the tree so that the resulting tree satisfies the definition of a BST. You are supposed to output the level order traversal sequence of that tree. The sample is illustrated by Figure 1 and 2.
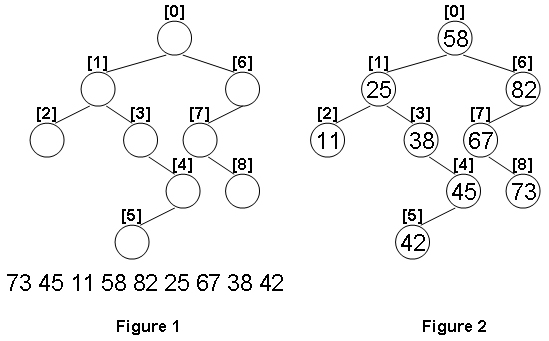
Input Specification:
Each input file contains one test case. For each case, the first line gives a positive integer N (<=100) which is the total number of nodes in the tree. The next N lines each contains the left and the right children of a node in the format "left_index right_index", provided that the nodes are numbered from 0 to N-1, and 0 is always the root. If one child is missing, then -1 will represent the NULL child pointer. Finally N distinct integer keys are given in the last line.
Output Specification:
For each test case, print in one line the level order traversal sequence of that tree. All the numbers must be separated by a space, with no extra space at the end of the line.
Sample Input:
9 1 6 2 3 -1 -1 -1 4 5 -1 -1 -1 7 -1 -1 8 -1 -1 73 45 11 58 82 25 67 38 42
Sample Output:
58 25 82 11 38 67 45 73 42
-
先建树 再中序遍历 同时数列排序放到对应中序位置 最后层序遍历
#define DeBUG
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstring>
#include <cmath>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <algorithm>
#include <vector>
#include <stack>
#include <queue>
#include <string>
#include <set>
#include <sstream>
#include <map>
#include <list>
#include <bitset>
using namespace std ;
#define zero {0}
#define INF 0x3f3f3f3f
#define EPS 1e-6
#define TRUE true
#define FALSE false
typedef long long LL;
const double PI = acos(-1.0);
//#pragma comment(linker, "/STACK:102400000,102400000")
inline int sgn(double x) {return fabs(x) < EPS ? 0 : (x < 0 ? -1 : 1);}
#define N 100005
int tree[1000][3];
int num[1000];
int k;
void midorder(int x)
{
if (x == -1)
return;
midorder(tree[x][0]);
// printf("%d ", x);
tree[x][2] = num[k++];
midorder(tree[x][1]);
return;
}
int ans[1000];
int ansnum;
void layerorder()
{
queue<int>Q;
Q.push(0);
ansnum = 0;
while (!Q.empty())
{
int now = Q.front();
Q.pop();
ans[ansnum++] = tree[now][2];
if (tree[now][0] != -1)
Q.push(tree[now][0]);
if (tree[now][1] != -1)
Q.push(tree[now][1]);
}
return;
}
int main()
{
#ifdef DeBUGs
freopen("/Users/sky/Documents/sublime project/in.txt", "r", stdin);
#endif
int n;
while (scanf("%d", &n) + 1)
{
int a, b;
k = 0;
memset(tree, -1, sizeof(tree));
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
scanf("%d%d", &a, &b);
tree[i][0] = a;
tree[i][1] = b;
}
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
scanf("%d", &num[i]);
}
sort(num, num + n);
midorder(0);
layerorder();
printf("%d", ans[0]);
for (int i = 1; i < n; i++)
printf(" %d", ans[i] );
printf("\n");
}
return 0;
}

